Centralized Data Management Minimizes Chances of Design Errors and Redundancies

The design and development of PCBs have undergone a significant transformation from hand-drawn schematics and tape-up layouts to sophisticated technologies and collaborative workflows. However, the challenge of combating errors and redundancies has emerged due to increasing data sharing between teams.
Early PCB design methods were prone to inaccuracies due to physical layouts, varied component libraries, and revisions leading to information loss. Digital schematics and layout software improved design tools but kept data siloed, leading to version control issues, outdated component information, and difficulty tracking design changes.
The Impact of Centralized Data Management on PCB Design
This product data management (PDM) is pivotal in operations today, and by establishing a central repository, companies will find several benefits:
- Reduced errors: Real-time data synchronization eliminates inconsistencies and outdated information, which reduces the risk of design errors.
- Collaboration: Previously siloed teams have immediate access to the latest design files, allowing for unhindered collaboration and faster development cycles.
- Optimized component reuse: Standardized libraries within PLM mitigate the risk of redundant component selection and guarantee quality consistency across projects.
- Improved traceability: Version control features help teams streamline revision history and identify potential issues through tracked design changes.
- Streamlined manufacturing: PLM feeds data directly into manufacturing software to reduce errors and speed up production.
Benefits aside, PDM does still have some challenges to overcome, including implementation and configuration, as well as integration with existing tools, which can be time-consuming for companies that invest in the system; data migration, which often requires manual effort and data cleaning processes; and the necessity to reskill your existing workforce through training and the creation of proper procedures to ensure that human errors don’t occur during the adoption period.
Key Benefits for Individual Stakeholders
PDM impacts the tasks and responsibilities of many stakeholders in the PCB design and manufacturing process, including product lifecycle managers, electronics design engineers, and quality assurance and control teams. Each part of the product process benefits uniquely from effective PDM implementation, as seen below:
Product Lifecycle Managers
For product lifecycle managers, PDM offers improved visibility and control over every part of the product life cycle. Through a centralized repository of accurate, real-time data, managers can track progress, identify potential bottlenecks, and make well-informed decisions at every stage; having this comprehensive oversight expedites decision-making processes and reduces time-to-market, thanks to streamlined processes and accelerated access to necessary data. That same access improved collaboration between stakeholders, with PDM synchronizing information across departments, from design to manufacturing and beyond. The net result? Reduced costs through minimized errors and rework, optimized material usage, and a more efficient process.
Electronic Design Engineers
PDM is a catalyst for improved design standards and efficiency among electronic design engineers. It provides tools for managing design revisions and version control, helping engineers maintain the integrity of their designs, which results in fewer errors and higher-quality output. Easy access to component libraries, standards, and historical data also helps them to work more efficiently, avoiding redundant efforts and optimizing productivity in the right areas. Historical data and product iterations prove particularly beneficial for engineers who want to reuse existing designs and components to reduce development time and cost.
Quality Assurance and Control
For quality assurance and control teams, PDM helps guarantee the integrity and reliability of PCB. Through the traceability of components and materials used in each design, PDM facilitates thorough quality control measures, helping teams to conduct root cause analysis (RCA) and defect prevention measures. It also aids in streamlining compliance efforts by managing tracking and adherence to relevant regulations and industry standards, mitigating potential risks, and guaranteeing product safety in accordance with the countries where they are distributed.
Operational Excellence through PLM and ECAD Integration
By integrating PLM and Electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), companies can create a powerful synergy for product development. It removes the wall between different silos in the process and enables a smoother flow of information. Electrical schematics and PCB layouts stored in PLM, for example, are made instantly accessible to designers, manufacturers, and suppliers, drastically improving collaboration across teams, eliminating manual data entry errors, and guaranteeing consistency in component lists. It brings real-time visibility into component availability and pricing changes, which allows teams to adjust designs to suit fluctuating markets and source available parts faster—an integrated approach that streamlines the product life cycle, leading to faster time-to-market, reduced costs, and improved quality.
Looking specifically at time-to-market and production efficiency, as well as BOMs, PLM shines for many reasons:
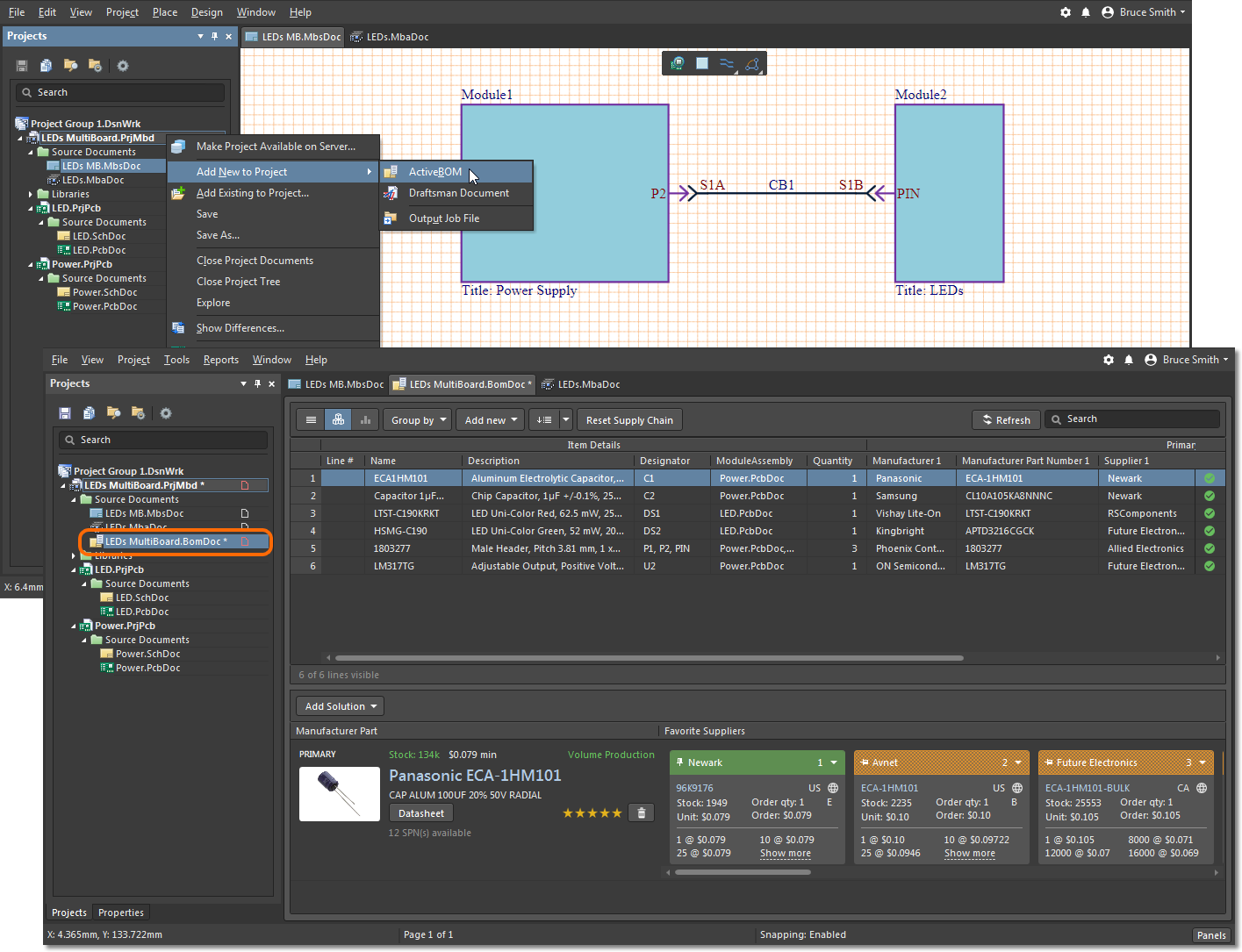
BOMs for Comprehensive Product Overviews:
- Single Source of Truth: PLM and ECAD integrations’ elimination of siloed data creates a single, trusted source for BOM information, guaranteeing all stakeholders work with the latest, accurate BOM, reducing the risk of errors and rework.
- Automated BOM generation: ECAD data is fed into PLM systems to generate the BOM automatically. This eliminates manual data entry, reducing the risk of human error and saving time.
- Advanced BOM functionality: PLM, through PDM, provides multi-level BOM, where-used reports, and cost analysis, giving stakeholders a deeper understanding of the product structure and cost breakdowns.
- Real-time change management: Changes made in either system are automatically updated on the other, keeping all stakeholders up-to-date and ensuring they have the latest BOM information. This reduces delays and improves collaboration.
- Component lifecycle management: PLM tracks component life cycles and alerts designers and engineers to obsolescence issues. It then suggests alternative options to keep the product development on track.
Enhancing Production Efficiency and Reducing Time-to-Market:
- Streamlined data transfer: Direct communication between PLM and ECAD guarantees data integrity and reduces time spent manually transferring information.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM) rules: PLM also integrates DFM rules to help designers avoid manufacturing limitations, thus reducing rework and optimizing potential yield.
- Production planning and scheduling: PLM provides production planning and scheduling tools that ensure the timely availability of materials and optimize production flow, speeding up turnaround time.
- Improved collaboration: Integrated systems facilitate collaboration between design, manufacturing, and procurement teams, helping them to resolve problems and approve changes quicker.
- Change impact analysis: PLM analyzes the impact of design changes in the BOM and production process to minimize disruption and facilitate smoother implementation.
Remember that the success of PLM and ECAD integration depends on choosing the right solution and arranging efficient implementation and user training. But by leveraging this integration, PCB manufacturers can achieve operational excellence, gain a competitive edge in the market, and deliver high-quality products faster and more efficiently to the increasingly demanding consumers.
Emerging Trends and Technologies in PLM Integration with PCB Design
There are many developments to come in the PLM space; it’s continuously changing to suit new norms and needs. At the moment, significant strides have been made in streamlining data management and collaboration, but there’s more to come as new, infantile technologies start to enhance PLM’s capabilities:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are set to revolutionize the design process. How? Predictive maintenance can prevent costly downtime; design optimization algorithms can tailor solutions to specific needs and constraints; and AI-powered data analysis can uncover hidden patterns and potential issues in the production process.
The adoption of cloud-based PLM solutions is becoming more widespread, with companies slowly moving away from on-premise solutions in favor of breaking down geographical barriers and empowering remote collaboration. It’s accessible, scalable, can handle growing data volumes, and has enhanced security features handled by the vendor, making it attractive for growing businesses and incumbents alike.
The concept of digital twins levels up collaboration. By creating virtual replicas of physical PCBs, teams can conduct virtual prototyping, monitor performance in real-time, and improve traceability throughout the product life cycle.
Collaborative design environments will also improve teamwork between silos through real-time editing, seamless version control, and integrated communication platforms. This will foster agility and innovation between disparate teams so that they can work together on projects.
Companies can optimize processes by pairing centralized data management through PLM with sophisticated collaboration tools. From streamlined manufacturing and better quality control to increased efficiency and faster time-to-market, the benefits are unequivocal. As we look forward and adopt incoming technologies, the future of PCB design promises remarkable efficiency, quality, and innovation. Now, amid a volatile market with a growing number of competitors, it is time to bridge the silos, connect your teams, and unlock the full potential of your company’s design journey.
To elevate your PCB design standards and unlock unparalleled efficiency and innovation, look at Altium Enterprise Solutions, where we bring digital transformation to life with a comprehensive, digitally integrated electronic design solution for enterprises.