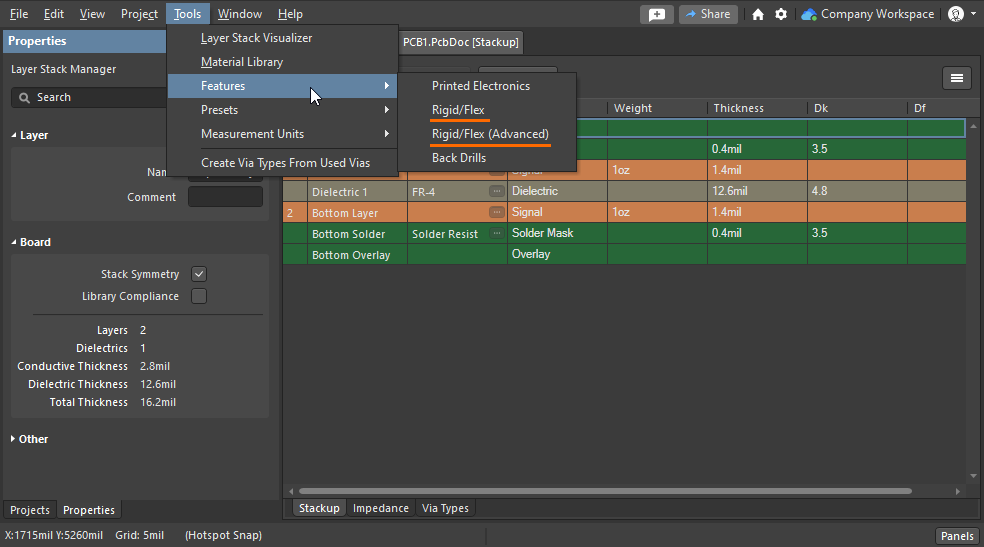
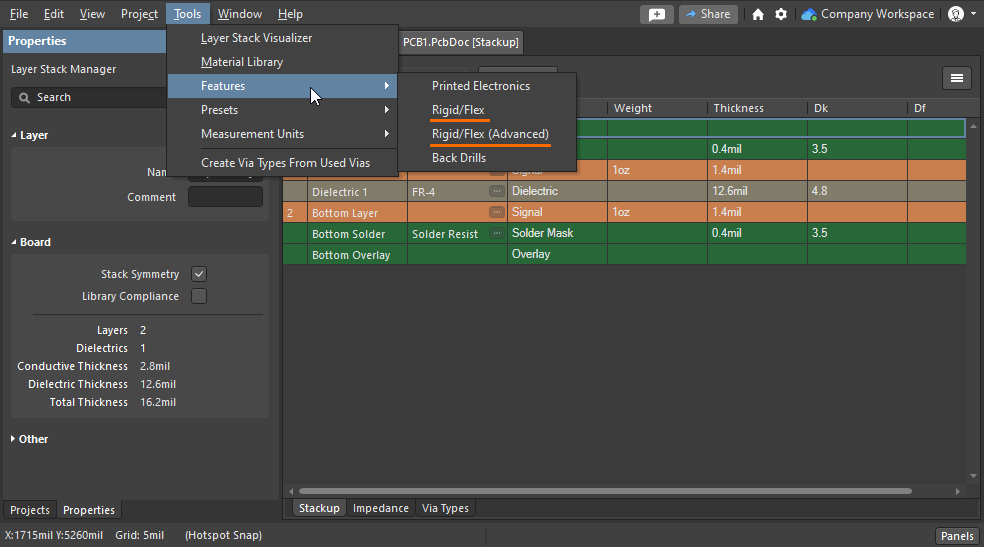
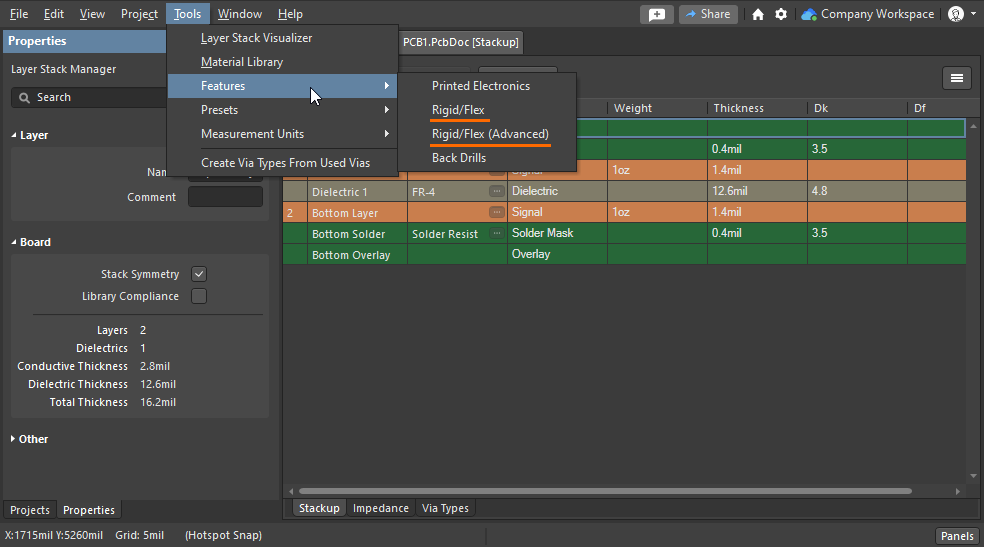
Rigid-Flex PCB Design Guidelines

Rigid-flex PCB technology offers tremendous benefits in terms of reduced weight and space, however flex assemblies can have greater durability and reliability. Today’s small lightweight consumer electronics products are best implemented with rigid-flex technology, however, there can be many challenges in achieving successful rigid-flex PCB designs. This guidebook is an attempt to clearly explain the materials, processes and design issues in a way that will enlighten PCB designers of any level.This paper highlights several key considerations for rigid-flex design.
Rigid-flex PCBs are a time-proven, well-understood technology initially used within the military/aerospace industry decades ago. Today, it is recognized as an ideal solution in electronics assemblies with small form factor and in highly durable, lightweight electronic products such as wearables, medical devices, and mobile wireless products. However, as many PCB designers contemplate designing rigid-flex PCBs for the first time, several challenges come to mind:
- How much will rigid-flex cost to fabricate and assemble?
- How are dissimilar rigid and flex sections described in a single PCB assembly?
- How are the different rigid and flex materials and layer specifics managed and communicated to a fabricator?
- How can the range of flex motion and critical folding lines be modeled and verified?
- How are placement and routing within flex regions different from that of traditional rigid PCBs?
These and many other questions reflect the challenges of rigid-flex PCB design. In this e-book, readers will gain a thorough look at flexible printed circuit materials, fabrication processes, and design challenges. The goal is to give readers a point of reference to help answer these questions and design reliable flex PCBAs that can be produced with maximum yield.
Click the PDF below to read more about PCB reliability and testing. You can also read the original, full-length content here:
Flexible Circuits: Getting Started with a Flex Circuit Design Guide
Introduction to Flex PCB Materials
The Rigid-Flex PCB Manufacturing and Fabrication Process
Flexible Printed Circuit Design Best Practices
Preparing Rigid-Flex PCB Documentation for Manufacturing
Flex and Rigid-Flex PCB Applications
Support for Rigid-Flex in Altium Designer

 Open as PDF
Open as PDF