How to Create a PCB Layout from a Schematic in Altium Designer

You’ve done your usual excellent job of putting together the PCB schematic. The circuitry is defined and you are ready to go to PCB layout. But this time it’s a little different. Maybe your regular layout resources aren’t available, or perhaps you want to try to do your first layout yourself. Whatever the reason, you are ready to start working on the board side of PCB design, but you’re not sure how to create it from a PCB schematic in Altium Designer.
Fortunately, the next step in Altium Designer is very straightforward. We’ll take a look here at a very simple PCB schematic and see what needs to be done to synchronize it with a brand new PCB design. This simple little design probably won’t be anything like the schematics that you are working on, but the basic steps of data transfer from schematic to circuit board will be the same. Creating a PCB layout from a PCB schematic doesn’t have to be difficult, and Altium Designer can serve as your all-in-one schematic to PCB converter.
How to Convert Schematic to PCB Layout in Altium Designer
The process for how to convert a schematic to a PCB layout in Altium Designer follows three simple steps:
Step 1 is intended to check your schematic for design rule violations that keep your schematic from being synchronized with your PCB layout. Once your PCB layout is created, this first synchronization step will ensure that any later change in the schematic can be immediately imported into the PCB layout. Step 2 involves using the schematic editor to import the board into a blank PCB layout. You'll need to create a new PCB file in your current project, and then use the schematic editor to import footprints for your components into your new PCB. In Step 3, you'll define a layer stack for your new PCB. Once you've completed these three steps, you can now start arranging components and routing traces between them.
Can You Import an Existing Schematic File to a New PCB in Altium Designer?
The answer is: Yes! If you have an existing schematic file from another project, and you want to import the schematic to a new PCB, you can simply add the existing schematic file to a new project and follow the three steps above. You won't need to recreate the schematic. If you want to import an existing schematic to a new layout in Altium Designer, be sure to follow some best practices for design reuse. Read more about design reuse in this article.
If you've decided to go the design reuse route and import a schematic to a new PCB, you should make sure you have created libraries for your PCB schematic symbols and footprints for your components. This is especially important if you are using specialty components that are not found in the default set of component libraries in Altium Designer. This is also important if you want to reuse a PCB schematic that was made by another PCB designer.
What Can You Expect in a PCB Layout Editor?
Boards. Circuits. More boards. Traces everywhere, and the occasional flying monkey. Okay, maybe one of those doesn't belong.
In reality, the main thing you need to know to convert schematic to PCB layout is that you have access to components and component placement features, as well as traces and trace routing for copper placement. After these initial requirements are met, you’ll want access to printed circuit views and file outputs like PCB footprints, Gerber files and 3D modelling.
In an ideal setting, you'll convert a schematic to a PCB with your schematic editor and translate it easily into a finished layout. Then you’ll be able to work through your components, copper setting, ECAD/MCAD design team interventions and purchasing requirements to optimize your PCB design files for manufacturing.
As part of this process, Altium Designer includes several important design that help ensure your create an error-free PCB design from a schematic. You'll be able to quickly check your Altium Designer layout against your design rules and constraints, easily define your layer stack, run simulations of your design, and much more. Altium Designer's integrated design tools are designed to keep your PCB schematic and layout synchronized without using an external program for schematic capture, which efficiently streamlines the PCB schematic to circuit board process.
Watch this video for a quick demonstration on how to get started with the very basics so you can learn how to create PCB from schematic in Altium Designer:

Now let's take a look at how to import a schematic to a PCB in Altium Designer:
Step 1: Preparing to Synchronize the Design
The first thing to do is to give your PCB schematic one final review to make sure it's ready to begin the layout. This obviously doesn’t mean that you are finished with the front-end design and schematic capture--there will most likely be many changes before you are ready to go out for manufacturing. But you do want to make sure that there aren’t going to be any surprises in layout. Take a look for duplicated circuitry like forgotten copies, parts that should have been deleted, etc.
Now let’s make sure that the schematic checks out OK using the checking process in Altium Designer’s PCB schematic editor. To do this we will want to compile the schematic which will generate all the internal details of the design such as connectivity mapping between components and nets. While the design is being compiled, a host of different checks will be run to verify the PCB schematic to the design rules. So before we compile, let’s take a look at setting these rules up by going to the pulldown menu command; “Project > Project Options”.
The Project Options settings in Altium Designer
In the picture above, you can see a montage of the first four tabs of the options dialog box. First you have the ability to control which error you want to see and how it is reported. Next you can control which pin types are allowed to connect to each other, followed by the third tab which you can use to configure classes of nets and components. Lastly, you can see the tab which shows the settings for the comparator.
This controls how differences between the circuit board schematic and layout are reported and becomes important when you start adding extra design rules to your PCB. For the most part you will not make a lot of changes here, but you can find out details on configuring this in the documentation from Altium Designer.
Now you are ready to compile your PCB document schematic. Go to the “Project > Compile PCB Project…” pulldown menu to engage the compiler. If your design doesn’t have any errors in it, your PCB schematic design session will not return any messages.
In order to show you what an error looks like, we have removed a portion of the net that connects R1 to Q1 in the picture below and run the compiler. As you can see, Altium Designer has reported back to us that net “NetC1_1” only has one pin on it. Once I reconnected that net, the compiler ran without any reported errors as it should.
The compiler report of a design error
Step 2: Use the Schematic Editor to Import Design Data to a PCB
Now we are ready to convert schematic to PCB layout, but first we need a PCB to transfer too. Right click on the project and select “Add New to Project > PCB” as shown in the picture below. This will create a PCB object in your project tree. Once it is created, right click on it and save it as a new name, in my case I saved it as the same name as my schematic object.

Adding a new PCB object to the project in Altium Designer
With the PCB object created, you will now want to take some time and configure it the way that you want it to be to start your layout work with. First you will want to set up the grid that you need and set the origin of the printed circuit board layout. You will find the menu commands for this in the “View > Grids” pulldown menu and the “Edit > Origin” pulldown menu. You will also want to edit or recreate the board outline so that it is the size and shape that you need. To do this you will first change the board view from 2D to board planning mode in the “View” pulldown menu, and then use the use the appropriate editing commands in the “Design” pulldown menu.
At this point you are ready to transfer the design data from the schematic to PCB design. Altium includes the schematic editor and the PCB editor in the same program, and there is a "schematic to PCB converter" command in the main menu. On the top menu in the PCB editor, select the “Design > Import Changes From…” pulldown menu command. You will see the “Engineering Change Order” dialog box pop up as shown below.
The Engineering Change Order dialog box in Altium Designer
First click on the “Validate Changes” button on the lower left side of the dialog box. After Altium Designer has finished validating the changes that you are making by synchronizing the schematic data to the PCB, the “Check” column on the right of the dialog box will fill with green checkmarks indicating that those items and any schematic symbols that have successfully validated. Any items that do not validate will have to be investigated and corrected in order to get a fully synchronized design.
Next click the “Execute Changes button. It will take Altium Designer a moment to execute these changes, and you can watch the progress of the changes on the engineering change order dialog box. Once completed, all of the line items will have a green checkmark in the “Done” column as you can see in the picture below.
The Engineering Change Order dialog box after validating and executing the change
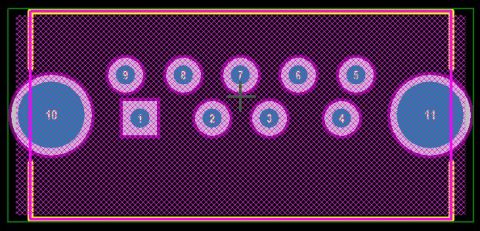
Congratulations, you have successfully transferred your design data from the schematic to circuit board. You can close the engineering change order dialog box now and you will see your components placed next to the board outline in a similar fashion to the picture below.
Schematic data has been successfully transferred to the layout and are ready to be placed
In the image above, you'll notice that the components are in the lower-right corner of the PCB editor window. When you import a schematic to a PCB in Altium Designer, the components will appear pseudo-randomly placed in the PCB editor window. Before you start arranging components around your printed circuit board, it's best to create your layer stack for your board and adjust the board size. You should do this now as your routing strategy may involve the use of vias, and you'll likely be using plane layers for power and ground. Go to the next step to create your layer stack.
Step 3: Define Your Layer Stack
Before you can proceed with layout, there are still some more tasks to do. Thinking about your components and reference designators, gathering your required information on your components and confirming with suppliers is necessary. You will also want to configure the PCB for the physical stackup of board layers, the display of those layers, and the design rules.

The Layer Stack Manager in Altium Designer
Above, you can see the layer stack manager in Altium Designer. You will find this command in the “Design” pulldown menu. It will allow you to add, copy, delete, and move physical layers in the PCB stackup. You can add layers for signal routing, power planes, and dielectric layers of the board. The layer stack manager also provides you with an impedance calculator as well.
To set up your design rules use the “PCB Rules and Constraints Editor” found in the “Design” pulldown menu. Lastly you will want to configure the display of your PCB layers and objects using the “View Configuration” panel. Below is an example of the view configuration panel’s “Layers & Colors” tab.
The View Configuration panel in Altium Designer
Now that your PCB schematic data has been transferred to the layout, you are ready to start arranging components on your PCB. You can start dragging your components around your new PCB and create your PCB layout. Once you've arranged components, you can start routing traces between them with the routing features in Altium Designer.
The View Configuration panel shown above is very useful for expediting your layout process as it allows you to turn on specific layers while routing and arranging components. When placing components, it's best to turn on the surface layer, silk screen layer, mechanicals, and the ground plane layer you'll be using for reference. This helps prevent layout mistakes that can create signal integrity and grounding problems in your PCB. The View Configuration panel is extremely useful as you can toggle different layers on and off so that you can clearly see how you are arranging and routing components.
Altium Designer is the only PCB design software package that is built on a unified design environment, which allows you to easily create PCB from schematic as we’ve shown here. You can pass design data back and forth between the PCB and schematic; this makes many design tasks simpler and more productive. The easy transfer of design data from schematic to circuit board is just the start of all the benefits that Altium Designer will give you.
If you haven’t started using Altium Designer as your go-to PCB schematic and layout software, take your PCB project to the next level by talking to an expert at Altium Designer.





 Back
Back