From Rework to Revenue: Digital PCB DFMA
Modern product development demands speed and precision, but as learned from recent industry surveys, critical phases remain stuck in paper-driven, manual workflows. For PCB design and assembly, this reliance on outdated processes leads to poor Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA) practices, resulting in unnecessary cost, significant delays, and lost engineering time.
Altium’s solutions are engineered to close this gap, transforming a high-risk, low-yield manual process into a precise, digital workflow.
1. The High Cost of Poor DFMA: Three Critical Pain Points
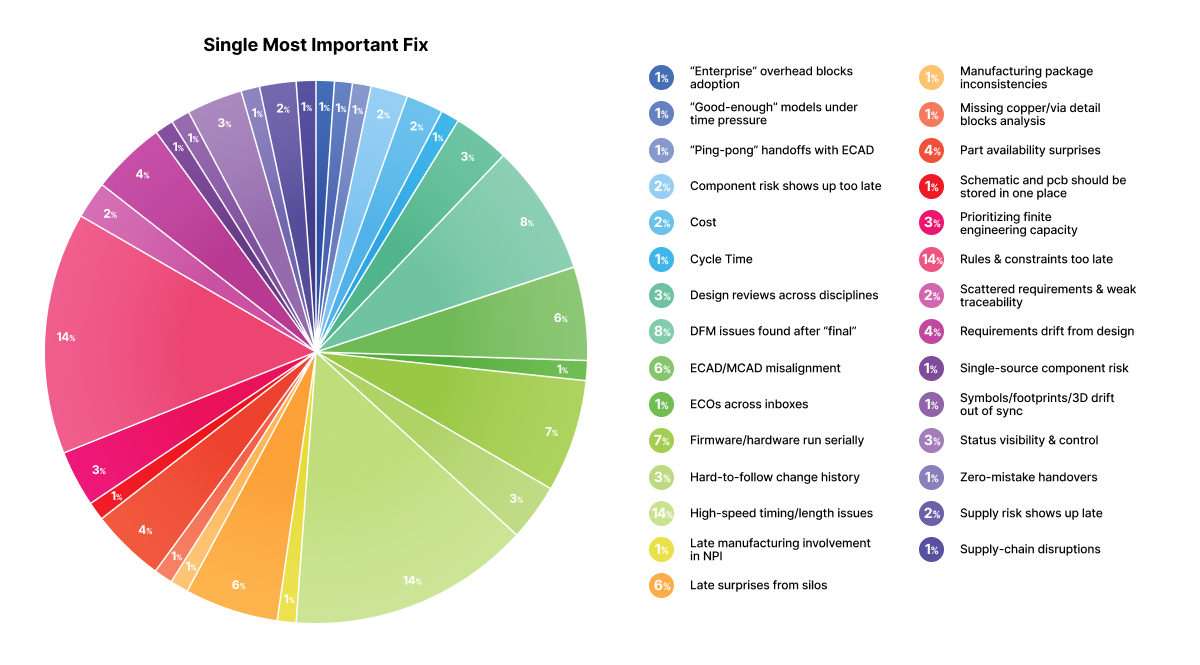
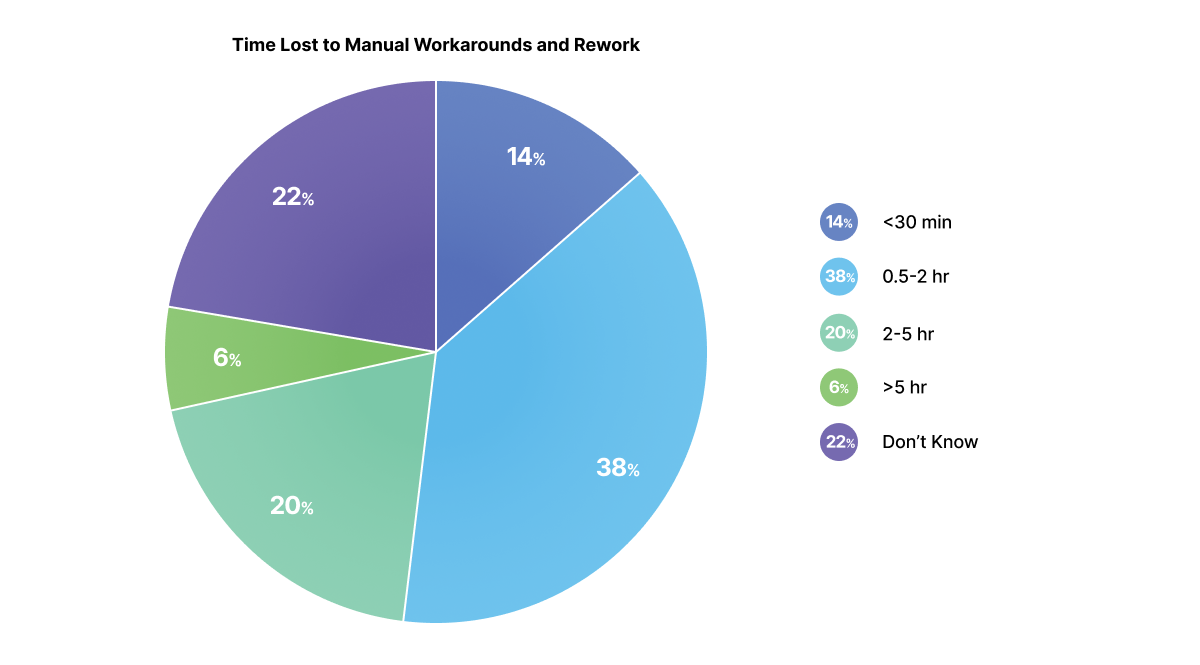
Our surveys reveal that designers and engineers are losing valuable hours every week due to core inefficiencies that digital solutions could easily resolve. These issues all stem from a fundamental breakdown in DFMA processes:
- The Upstream Rework Drain: The most significant drain on engineering resources is the rework caused by late-stage constraint introduction. Industry data reveals that critical DFM rules, mechanical boundaries, and operational constraints are often received and applied only after the PCB layout is well underway. This "shift-right" failure forces designers into expensive, disruptive re-layout cycles, dramatically impacting the project schedule and profitability.
- The Communication Gap: Engineers cited significant time lost due to cross-functional collaboration failures. When design, procurement, and manufacturing rely on emails, phone calls, and static documents to communicate changes, the workflow collapses.
- The Risk of Outdated Information: Engineers often resort to using manual, error-prone workarounds. This elevates the risk of using outdated design data and eliminates any chance of consistent yield forecasting or quality control.
2. The Altium Solution: Precision, Speed, and a Digital Thread
Altium's tools, specifically the Assembly Assistant within the Altium 365 cloud platform, provide a digital solution that directly tackles these DFMA challenges by enforcing precision and maximizing efficiency from layout to prototype.
- Flawless Precision: Errors in component placement and rework, ensuring component placement is correct the first time.
- Maximized Speed: Time wasted due to manual setup and document switching, accelerating time-to-market and reducing prototype time.
- Guaranteed Data Integrity: Outdated or inaccurate documents, ensuring all users work from the latest design release.
3. Key Features That Digitalize Assembly and Manufacturing
The following Altium features translate theoretical DFMA principles into practical, actionable steps across the entire pipeline:
A. Error-Proofing the Assembly Floor (DFA)
- Assembly Assistant Cross-Probing and 3D Visualization: Achieves flawless assembly through visual guidance. By linking the BOM item to the physical board location, the system ensures precise component placement and prevents orientation errors.
- Assembly Assistant Web-Based Interface: Accelerates prototype and short-run production by providing low-friction access to designs, eliminating paper print-outs and the need for specialized ECAD software. Because Assembly Assistant operates on the centralized platform, it guarantees assembly is always performed using the latest version-controlled design and Bill of Materials (BOM).
B. Unified Collaboration and Traceability (DFM)
- Version-Controlled Release Packages: Ensures the fabricator or CM is always working from the validated design release, avoiding costly respins due to outdated files. Communication is attached directly to the design for enhanced traceability.
- Cross-Team Design Review: Facilitates cross-functional manufacturability checks early in the design cycle. Teams can identify and resolve potential DFM issues proactively before money is committed to fabrication.
C. Strategic Supply Chain Integration
- Supply Chain Management Tools: Enables collaboration between engineering and procurement to monitor component risks, availability, and compliance in real-time, preventing production disruption and delay.
- Multi-ECAD Support: Manages all ECAD release packages, including design data files from all five of the major ECAD tools, in one centralized cloud platform, ensuring a single source of truth and simplifying the manufacturing handoff for multi-tool teams.
Final Thoughts
Altium's tools provide the only way to reliably enforce robust DFMA principles during prototype and low-volume assembly, leading to significant time savings, guaranteed data integrity, and a faster time-to-market.
Stop prototyping in the past. Adopt the digital thread to take control of your assembly line.