The IPC Warning About Microvia Reliability for High Performance Products
Hopefully, by now, you have read the full Press Release from the IPC on March 6, 2019, about the warning of field and latent failures of high-profile HDI boards. IF not, the complete press release is available on I-Connect 007. [1]
What you may have seen is the warning statement which the IPC will be including in the upcoming IPC-6012E, Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards:
“There have been many examples of post-fabrication microvia failures over the last several years. Typically, these failures occur during reflow, however, they are often undetectable (latent) at room temperature. The further along the assembly process that the failures manifest themselves the more expensive they become. If they remain undetected until after the product is placed into service, they become a much greater cost risk, and more importantly, may pose a safety risk.”
DON’T PANIC! Let me explain the background of this warning.
For the last few years, a few OEMs have experienced a latent defect in their sophisticated HDI multilayers even though screened with our best available incoming inspection and test methodologies. This defect caused failures observed in:
- Post-Reflow In-Circuit Test
- During the “Box Level” Assembly Environment Stress Screening (ESS)
- When removed from storage
- In-Service (End-Customer Fielded Product)
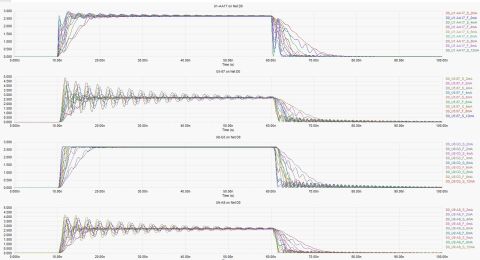
After much work and investigations by these OEMs, and with coordination with the D-32 Thermal Stress Test Methodology Subcommittee, the IPC issues a new test method for thermal stress, (IPC-TM-650, Method 2.6.27A) and thermal shock (IPC-TM-650, Method 2.6.7.2). The Method 2.6.27 calls for the test vehicle or coupon to be subjected to a normal solder paste reflow profile to reach a peak temperature of 230 degree C or 260 Degree C while under connection to a 4-wire resistance measuring unit for six (6) full reflow profiles without the increase of resistance of 5%. The daisy chain in the test coupon needs to be composed of features used in the actual circuits.
This has allowed these OEMs to detect the latent microvia failures and protect themselves from possible defect escapes. But finding the Root Cause of this latent HDI failure has been elusive. So, in early 2018, the IPC organized a select group of industry experts, under the supervision of Michael Carano, to investigate this situation. Later in 2018, this group was named the IPC V-TSL-MVIA Weak Interface Microvia Failure Technology Solutions Subcommittee. I am a founding member of this group. But let me emphasize,
During the past year, we have met and gone over test data, microsections and experimental results. Here is what we KNOW:
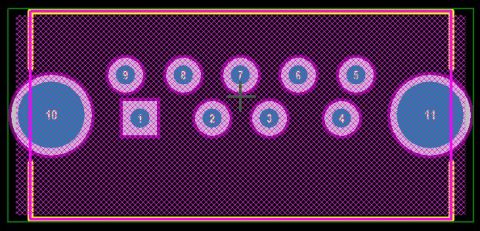
- The defect manifests itself as a fracture at the metallurgical interface of a microvia to the copper layer below it or to another microvia below it. (see Figure 1)
- First occurrence of the product-level failure detected (stacked microvias) 2010.
- Complex stacked microvias can exhibit this latent defect (>2 stacks) but not staggered microvias.
- Data thus far implies stacked microvia structures, especially stack-heights of 3 or greater, are much more likely to suffer this failure mode, and it is still a minority (but growing) percentage of high-reliability designs.
- Severity of end-use application environment (which we attempt to address by severity of test condition) appears to have some impact on the likelihood of occurrence.
- Several OEMs allow stacked FILLED vias if the design is no more than 2. Three is the tricky one.
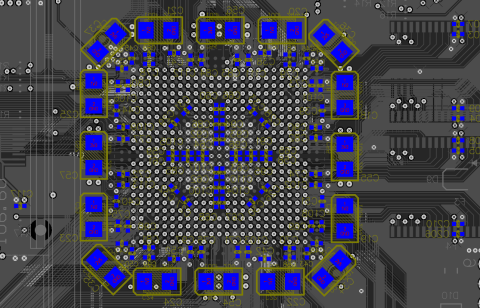
- This has been observed in complex HDI structures such as the 3-8-3 Qualification Coupon Design seen in Figure 2 below.
- Product-level failures are unpredictable (in-process, storage or filed)
- Historical industry-standard test methods were insufficient in detecting this failure but seem sufficient for normal HDI constructions.
- Preconditioning and thermal cycling may induce this defect but when it returns to room temperature, the defect is not detectable by 4-wire resistance measurements. Only when the PCB is brought up to reflow temperatures is it apparent.
- IPC TM-650 2.6.27A technique that duplicates assembly reflow will reliably detect this latent problem. (see Figure 3 below).
- Although the committee developed an FMEA for microvia defects, only this one WMI is our focus.
- Additional work by the committee or industry is needed to identify the root cause(s) and implement corrective actions. Volunteer’s for this committee are accepted provided they come to work. (contact Chris Jorgensen at IPC or Michael Carano at rbpchemical.net)
- Any industry data pertaining to this problem can be contributed to the IPC and will be used ‘anonymously’.
To further read about the WMI Committee and our findings, there is a report available from our APEX 2019 WMI OPEN FORUM [2] and a White Paper was published by the committee, IPC WP-023 “Via Chain Continuity Reflow Test: The Hidden Reliability Threat- Weak Microvia Interface.” Available from the IPC Bookstore.
Further discussions will be undertaken at the upcoming IPC Annual High-Reliability Forum to be held in Baltimore on May 14~16 [3]
FIGURE 1. The WMI latent defect observed after six reflows of 230 OC. [used with permission][4]
FIGURE 2. A complex HDI qualification coupon (3-8-3) with both stacked and staggered microvia structures. [used with permission] [4]
FIGURE 3. Reflow profile and 4-wire resistance of a 4+N+4 stacked microvia structure opening at only 224.6C and closing at 184C on cooling down. Subsequent room temperature testing and thermal cycling testing indicated no defect. [used with permission] [4]
Have more questions? Call an expert at Altium or learn more about how integrated design tools aid high-density PCB layout in Altium Designer®.
REFERENCES
- IPC Press Release, Mar 6, 2019
- Weak Microvia Interface Open Forum, IPC APEX, Jan 2019, San Diego, CA
- IPC High-Reliability Forum in Baltimore, MD on May 14-16, 2019
- J.R. Strickland & Jerry Magera, How MSI Applied Technology Beat the Microvia Hidden Threat, IPC High-Reliability Forum, May 16, 2018, Baltimore, MD