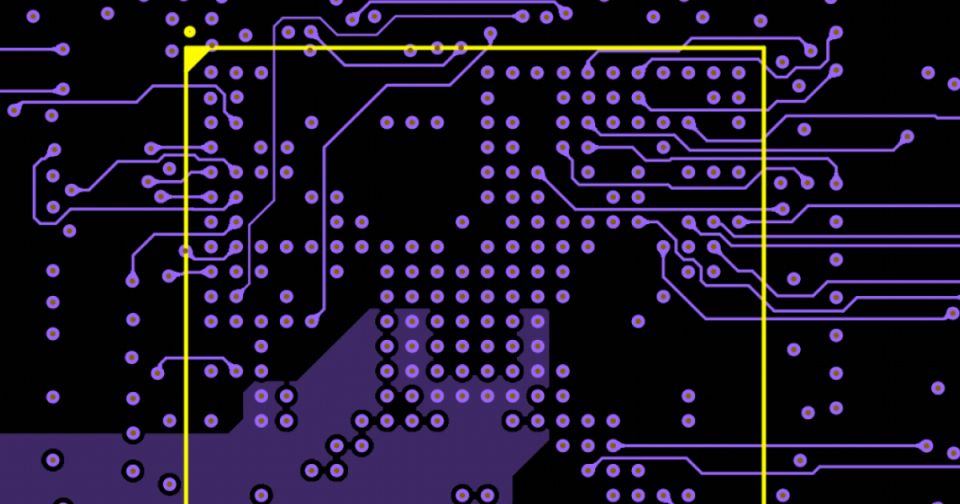
PCB Routing
Routing in your PCB makes copper connections between components, and best routing practices will help ensure signal integrity, low crosstalk, and low EMI. Browse our library of resources to learn more about routing in your PCB and how the best PCB layout software helps you obey routing rules and signaling standards.
Filter
found
Sort by